Evening Star: How to Set Your Stop-Loss
In this post, we'll explore effective strategies to set a stop-loss when using an evening star pattern to initiate a short position.
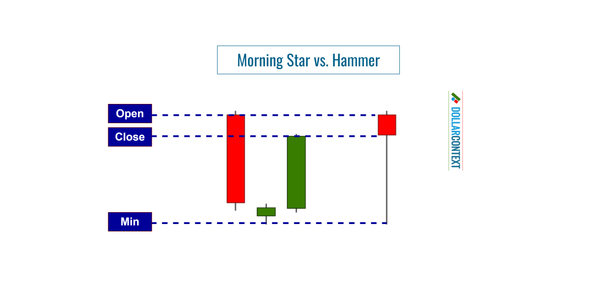
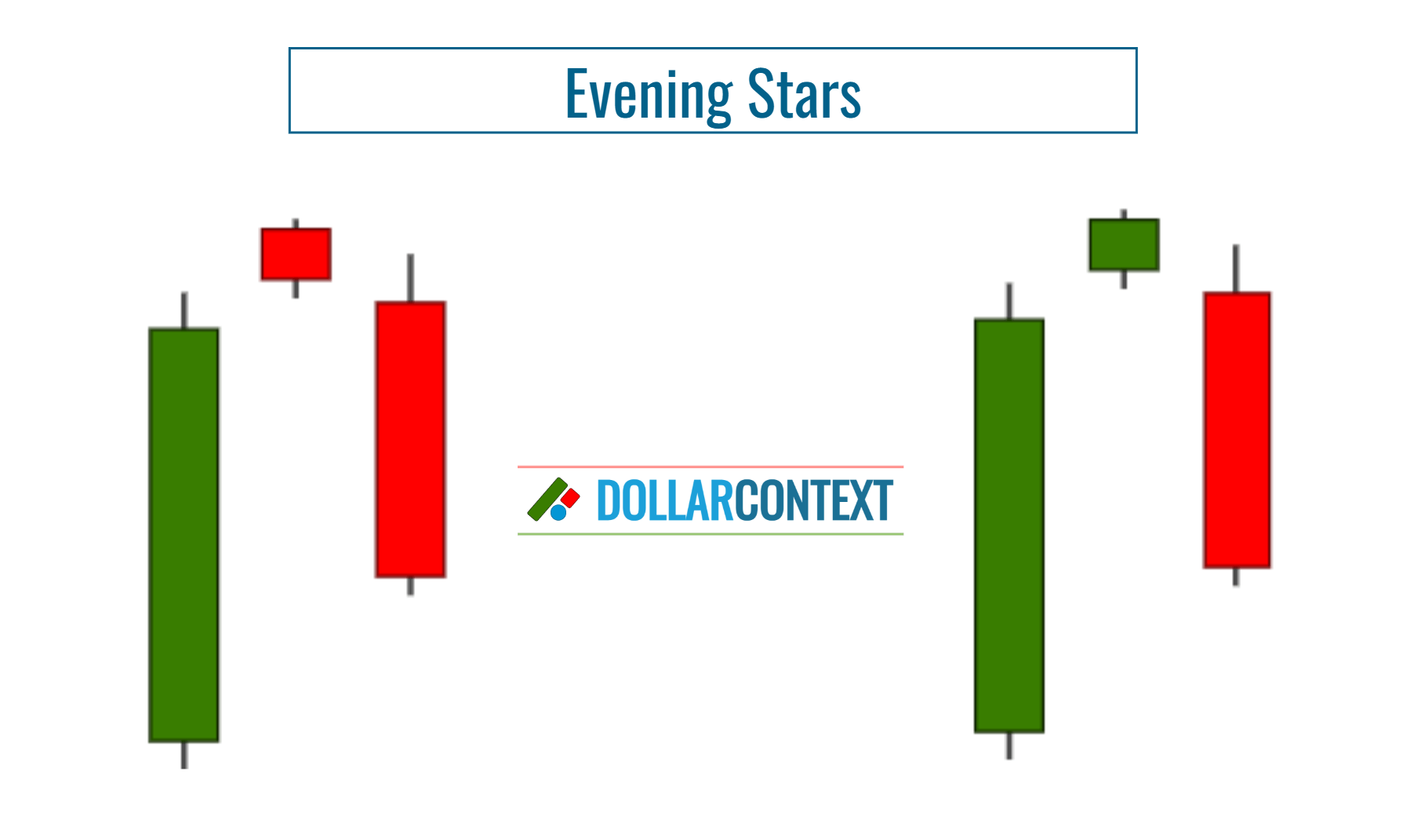
In Japanese candlestick analysis, the evening star is a bearish reversal pattern that occurs after an uptrend.
Here are detailed, step-by-step instructions for setting a stop loss when initiating a trade based on an evening star pattern.
1. Correct Identification
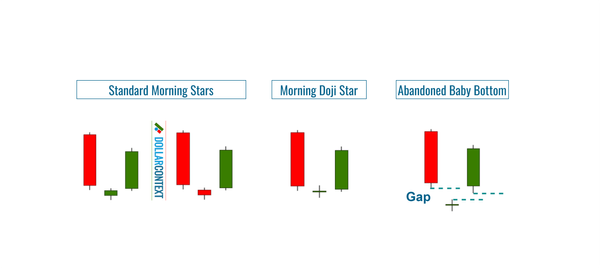
Make sure that you correctly identify the evening star on your chart. The pattern consists of three candlesticks that appear after an uptrend:
- A long bullish (green) candle, representing strong buying activity and continuation of the preceding uptrend.
- A small-bodied candle (which can be either bullish or bearish), signifying market indecision. Ideally, this candle should gap above the close of the first candle, showing a potential exhaustion of the bullish trend.
- A long bearish (red) candle, indicating strong selling activity and confirming the reversal. This candle usually closes well into the body of the first bullish candle.
2. Verify the Previous trend
From a psychological standpoint, an evening star signals a possible change in market mood. However, for a trend reversal to occur, a distinct upward trend must precede the evening star pattern.
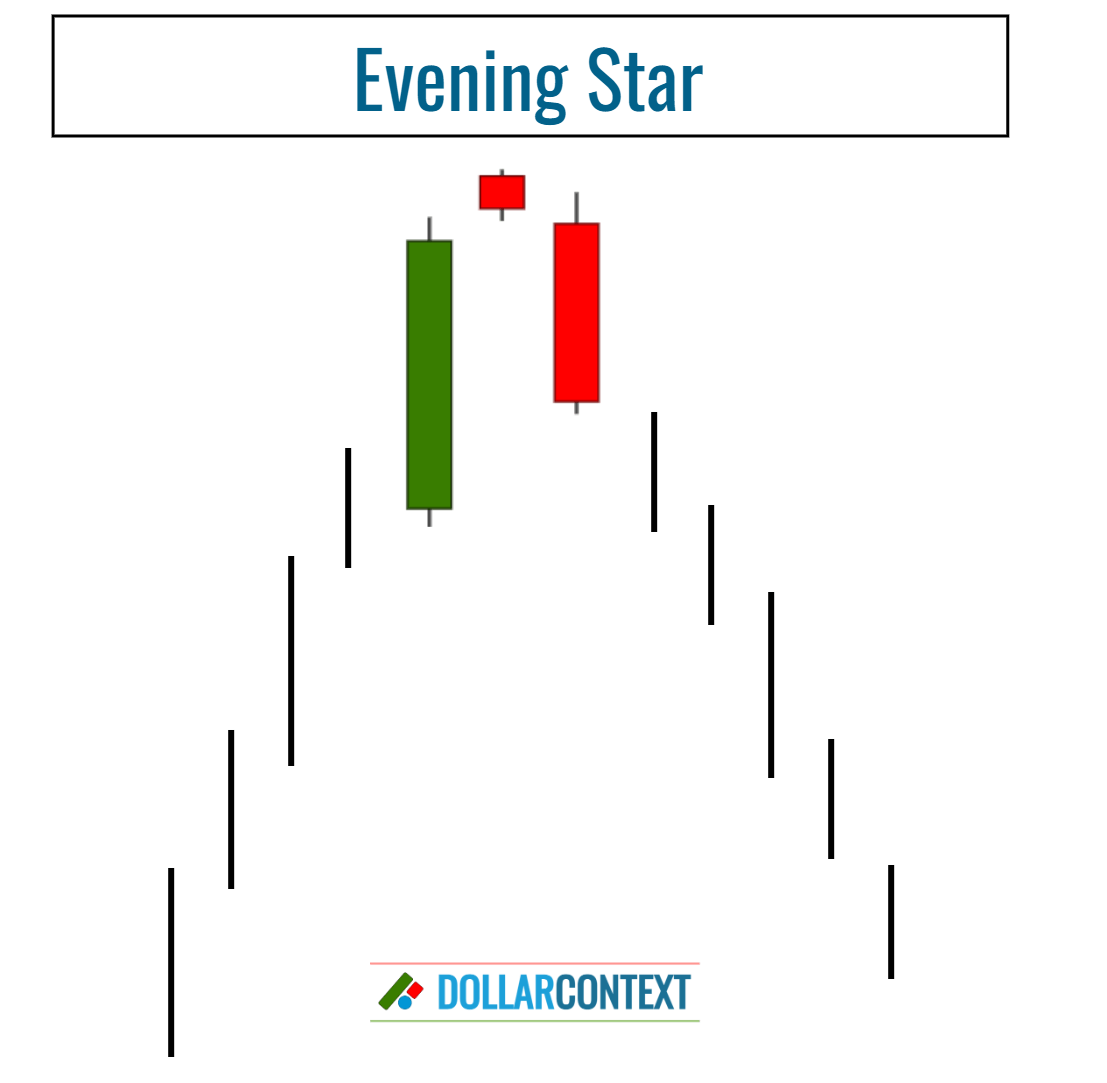
In a market that's trending sideways or showing a mild trend, an evening star generally carries little significance.
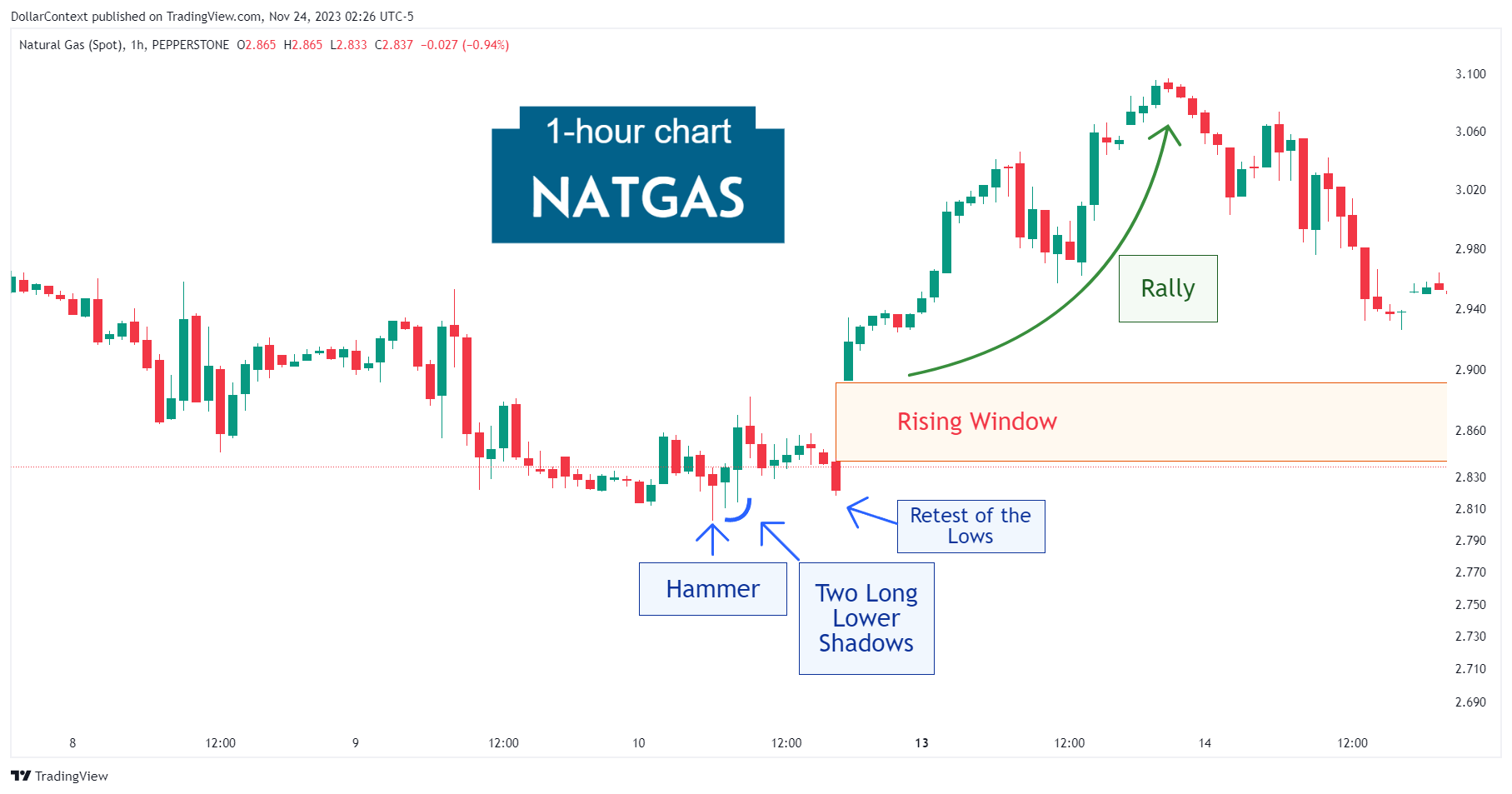
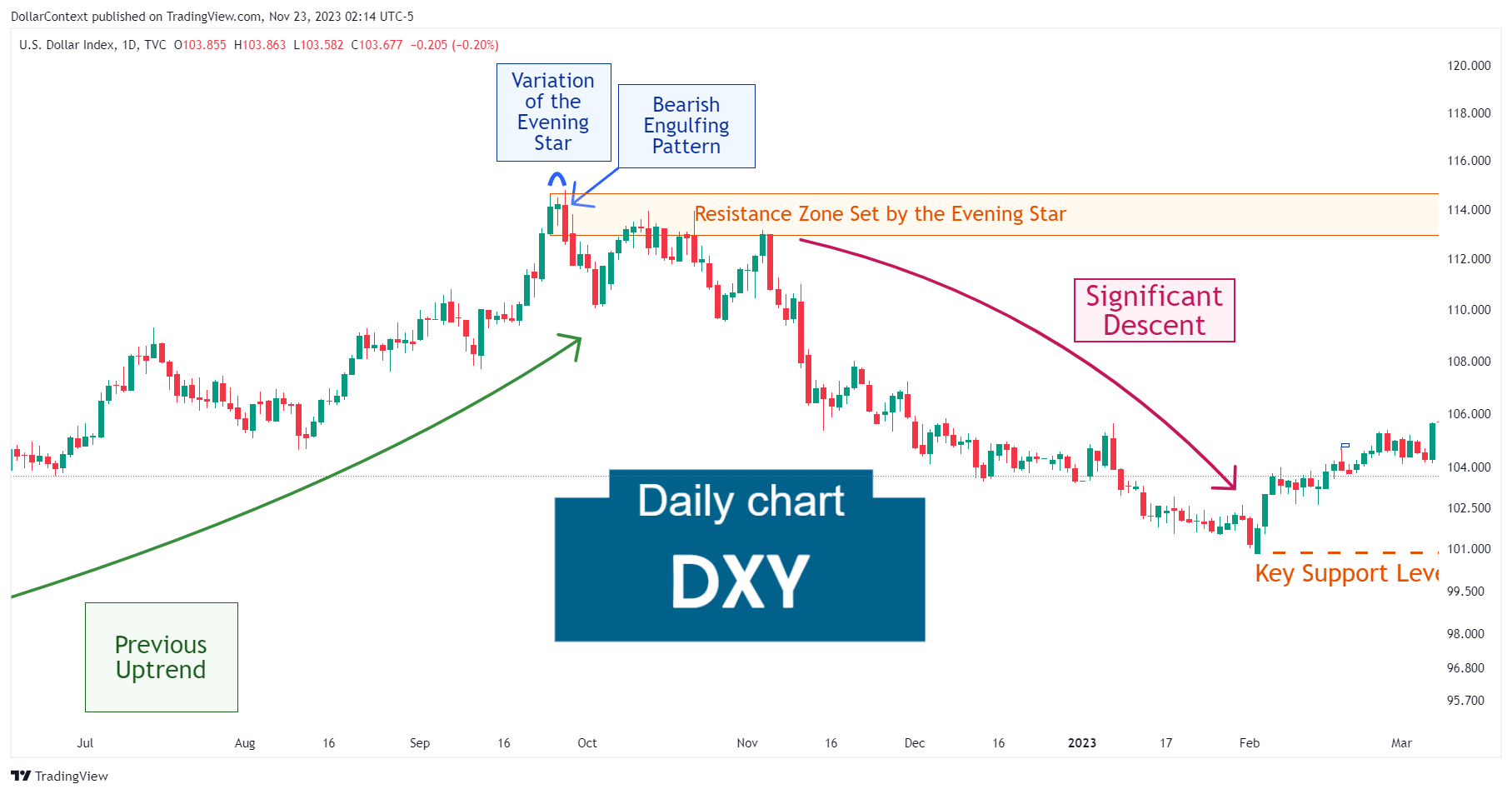
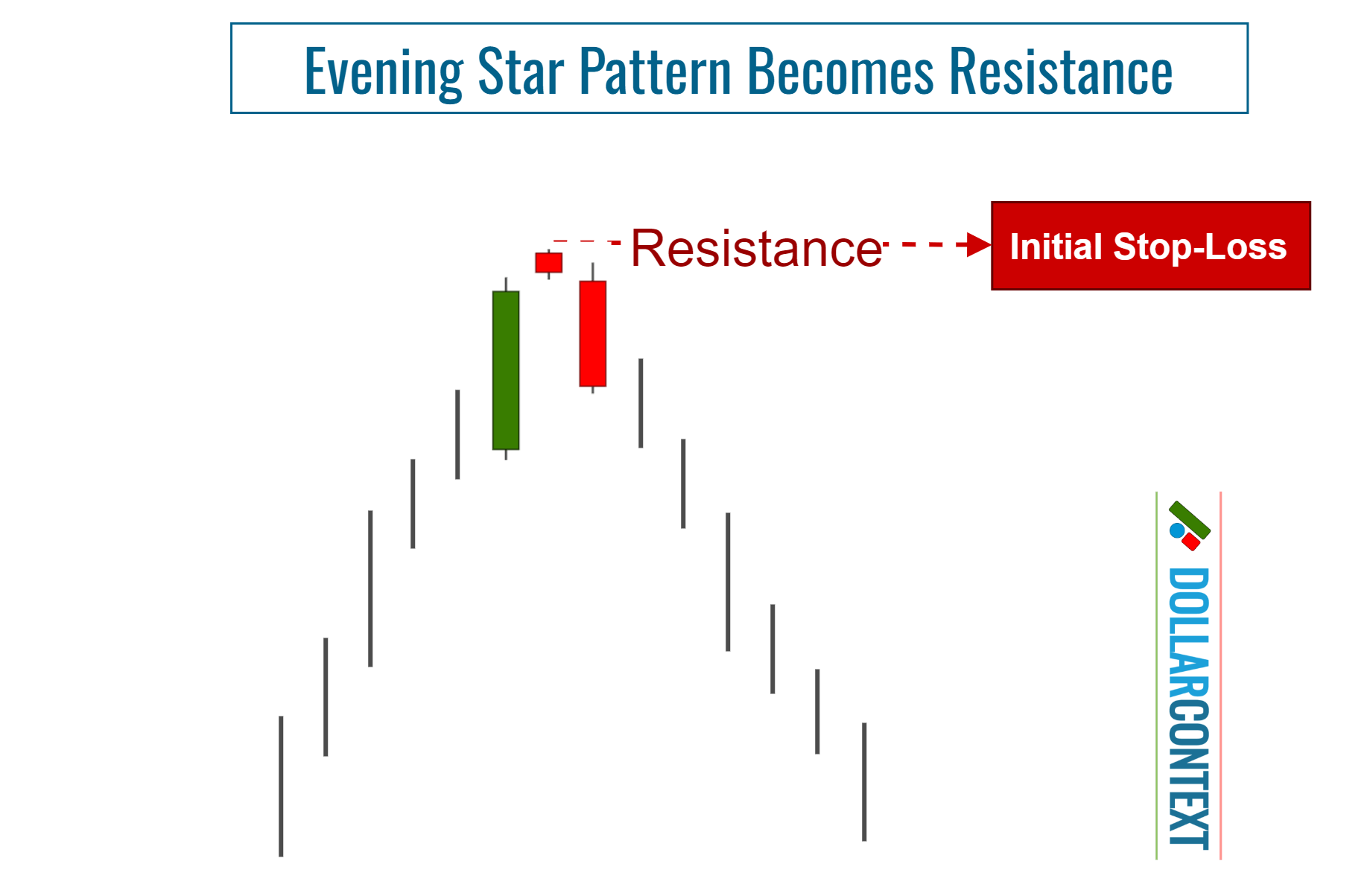
3. Identify the Resistance Zone
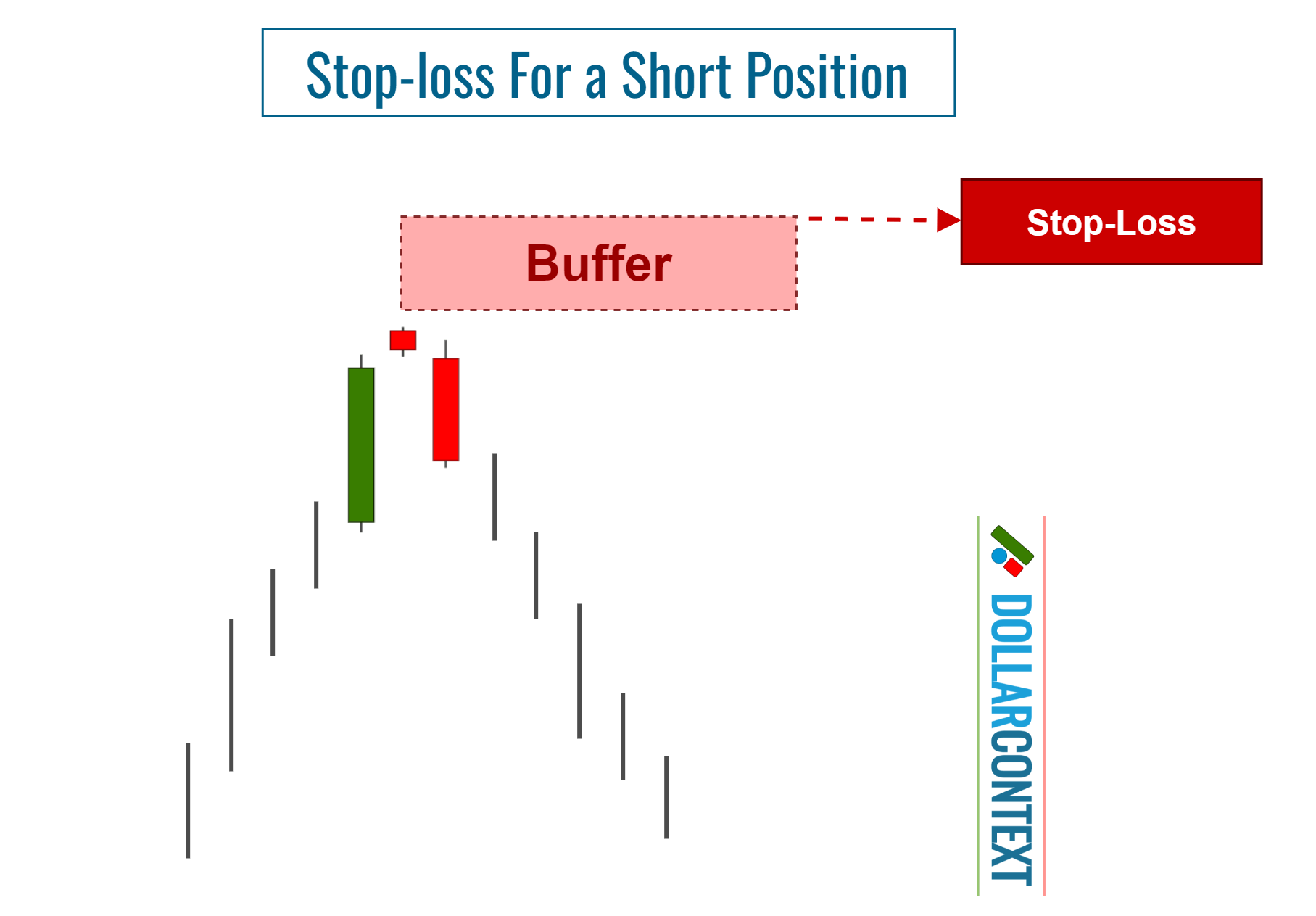
After an uptrend, the price range linked to an evening star becomes resistance. The highs of this range can serve as a reference point for setting your initial stop-loss when opening a short position.
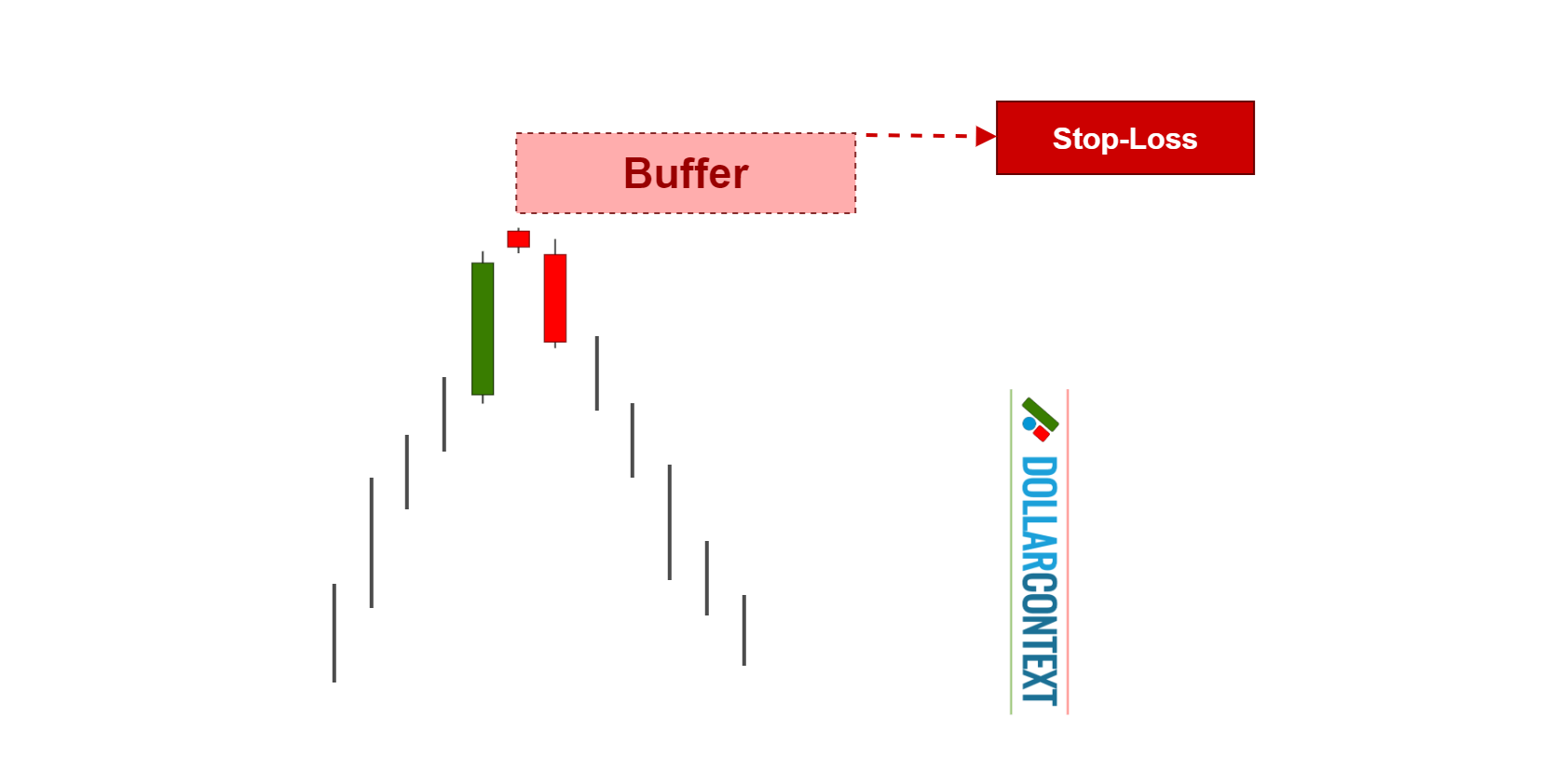
4. Consider Adding a Safety Margin
After considering elements like risk management and market volatility, you may choose to include a cushion to your initial stop-loss. This extra measure can help shield you from false breakouts effectively.
5. Determine If Your Stop-Loss Is Based on a Closing Price
A stop triggered at close is activated when the closing price of the session crosses the stop-loss level, instead of merely depending on intraday price movements.
In the realm of Japanese candlestick analysis, it is often recommended to set a stop at the closing price, especially when using an evening star to initiate your position.
6. Monitor the Trade
Regularly review both the market and your position to ensure they align with your evening star strategy. Specifically:
- Revise and Update Your Stop-Loss as Required: Markets are ever-changing, and new candlestick patterns could appear as your trade unfolds. In such instances, consider fine-tuning your stop-loss to suit the evolving landscape. For instance, if a new candlestick pattern emerges near the price range of the evening star, reinforcing the bearish reversal theory, adjusting your stop accordingly would be wise.
- Adjust as the Price Moves in Your Favor: Think about implementing a trailing stop-loss to safeguard profits and manage risk effectively.
- Maintain Discipline: Resist emotion-driven decisions, regardless of how the market behaves.