Upthrusts in Trading: Concept, Types, and Strategies
The upthrust is a powerful trading concept that can provide traders with insights into the potential change in market sentiment.
Approximately 70% of the time, it's estimated that markets are in a state of range-bound behavior. When the market is in a nontrending mode, it would be valuable to use a trading tool that provides attractive entry points. Upthrusts, a concept popularized by Richard Wyckoff in the early 20th century, is one of these tools.
Contents
1. What Is an Upthrust?
An upthrust is a price action in which the price of an asset briefly breaks above a defined trading range, or a key resistance level, but quickly retreats back down. This action traps traders who bought into the breakout, expecting the price to continue its upward trajectory.
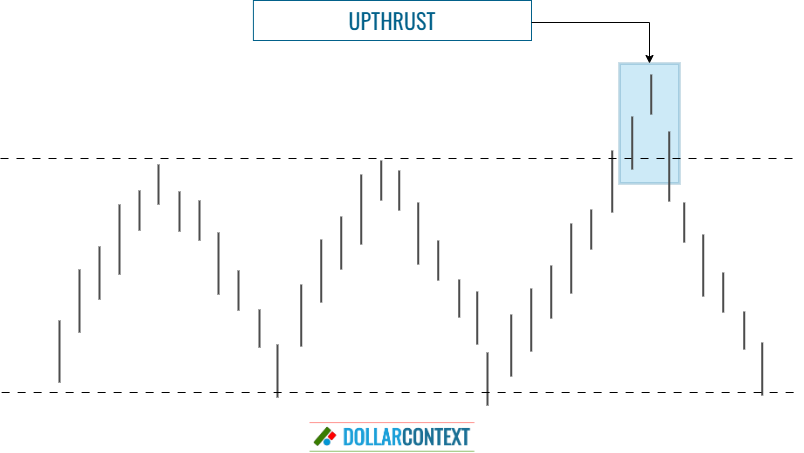
In technical analysis, an upthrust is the opposite of a spring. If an upthrust momentarily breaches a resistance level, a spring briefly surpasses a support level.
The characteristics of an upthrust include:
- Price Breaks Resistance: Initially, prices will move above a known resistance level.
- Volume Spike: As prices breach the resistance, there's often a notable increase in trading volume. This surge is due to traders buying into the breakout.
- A Rapid Reversal Occurs: After moving above the resistance, the price tends to quickly reverse back into the trading range, indicating a failure to maintain the breakout.
- Subsequent Decrease in Volume: As the price falls, the volume typically decreases, probably indicating a lack of interest in buying at higher prices.
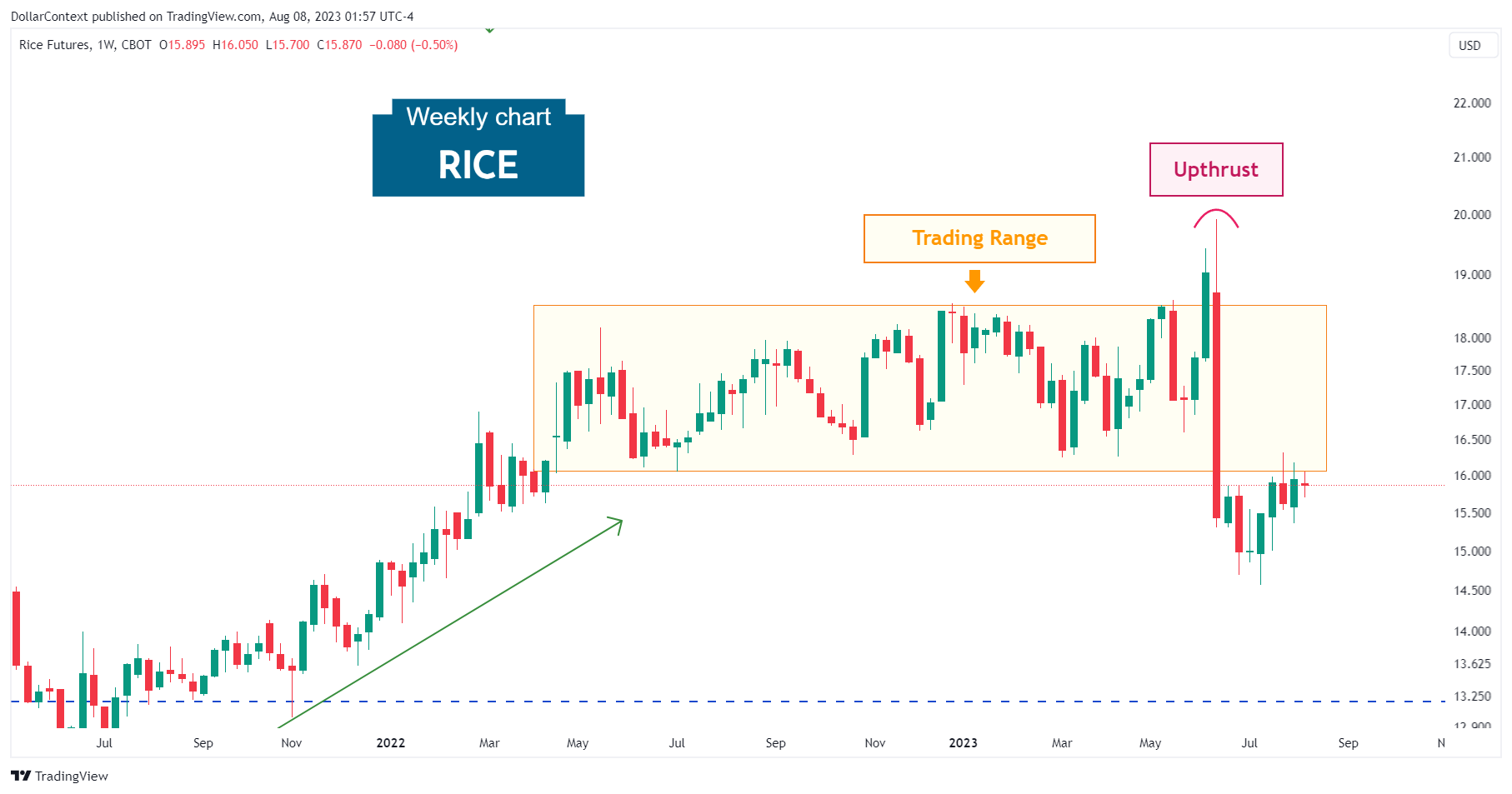
The following example shows a prolonged sideways trend in the rice market spanning more than a year. By June 2023, the price exhibited an upthrust, which was followed by a swift reversion back into the previous range.
2. Types of Upthrusts
Upthrusts in the market can take on different shapes and magnitudes, which in turn are influenced by a number of factors, including:
- Context
- Speed
- Magnitude
- Area of Technical Analysis
- Outcome
2.1 Context
Based on the context in which an upthrust emerges, we can differentiate between:
- Trading Range Upthrusts: These are upthrusts that emerge during a trading range period.
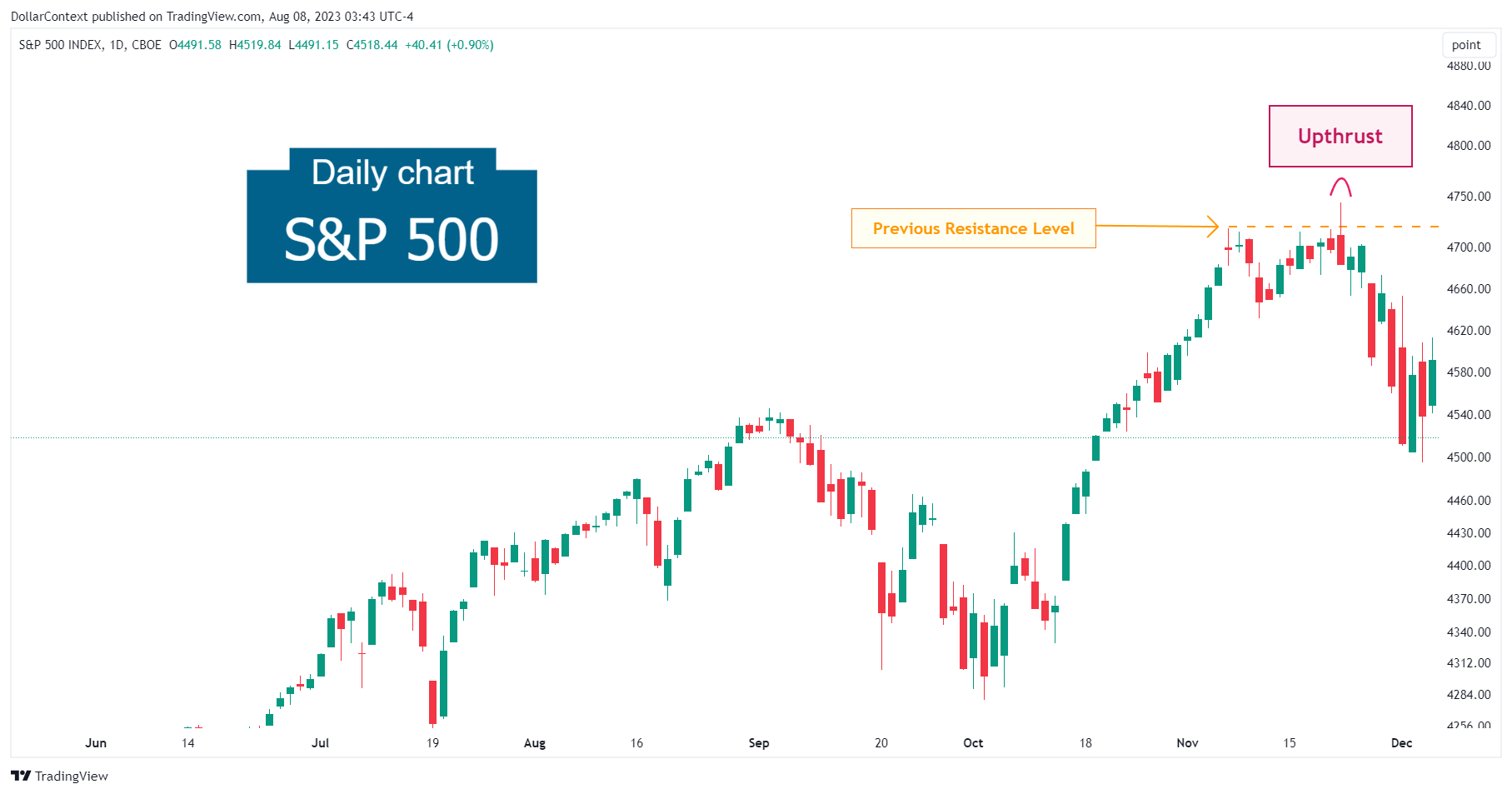
- Resistance Level Upthrusts: An upthrust appeared in relation to a prior resistance level, distinct from the upper limit of a lateral range.
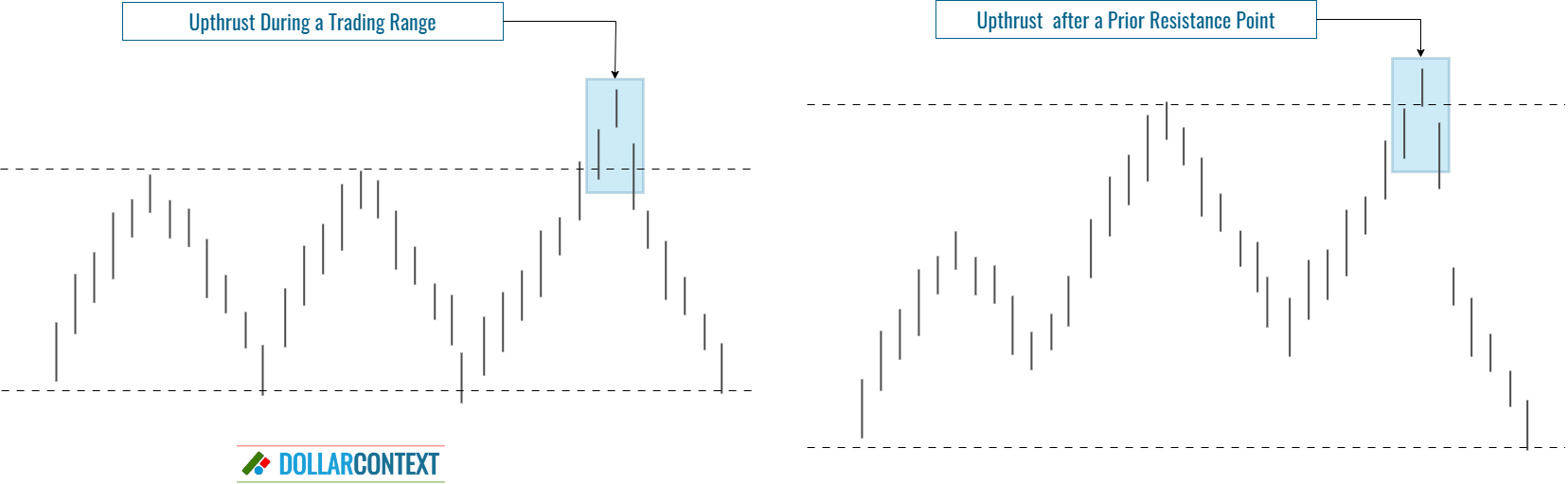
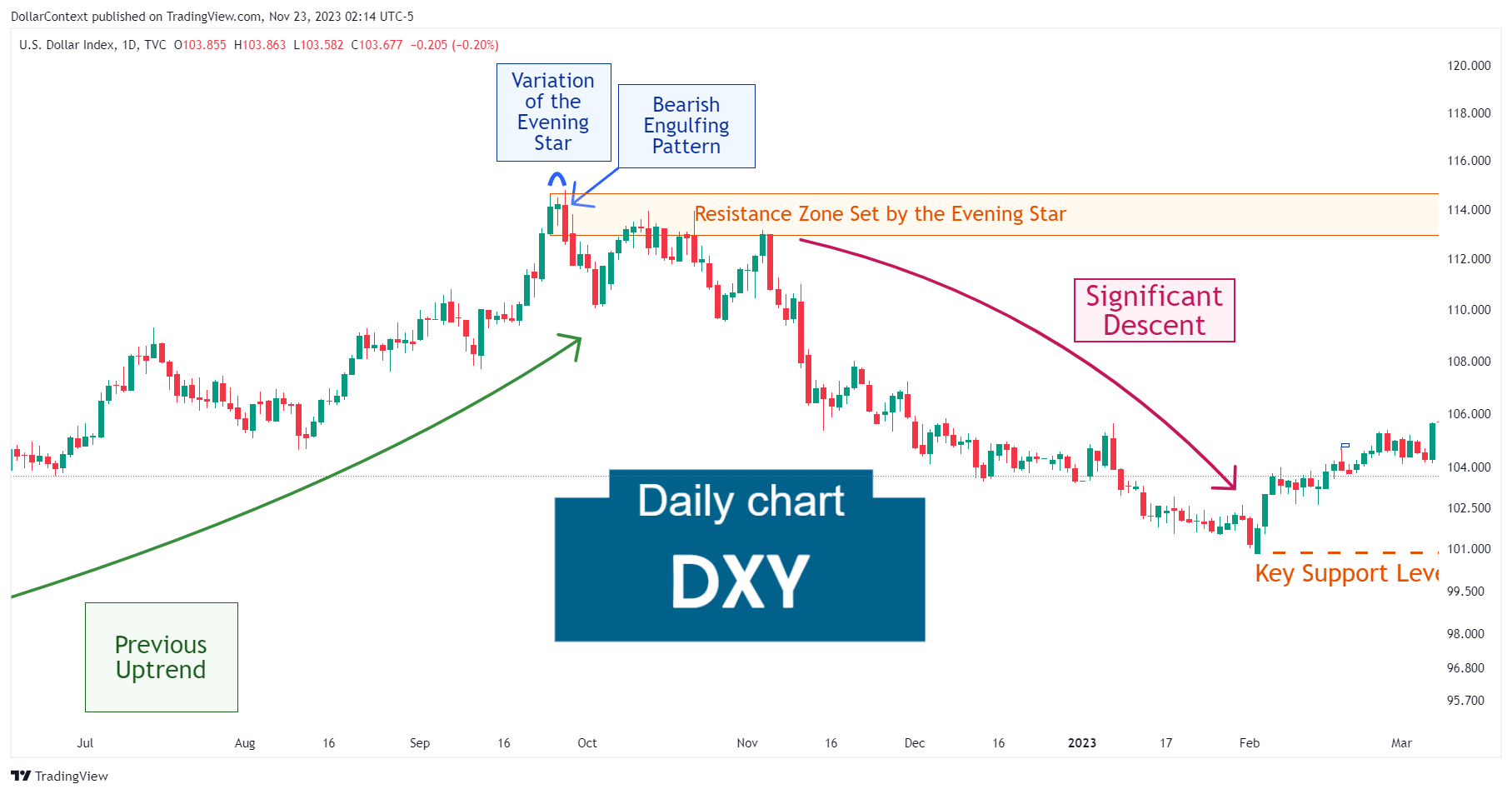
This example shows an upthrust after a previously established resistance mark.
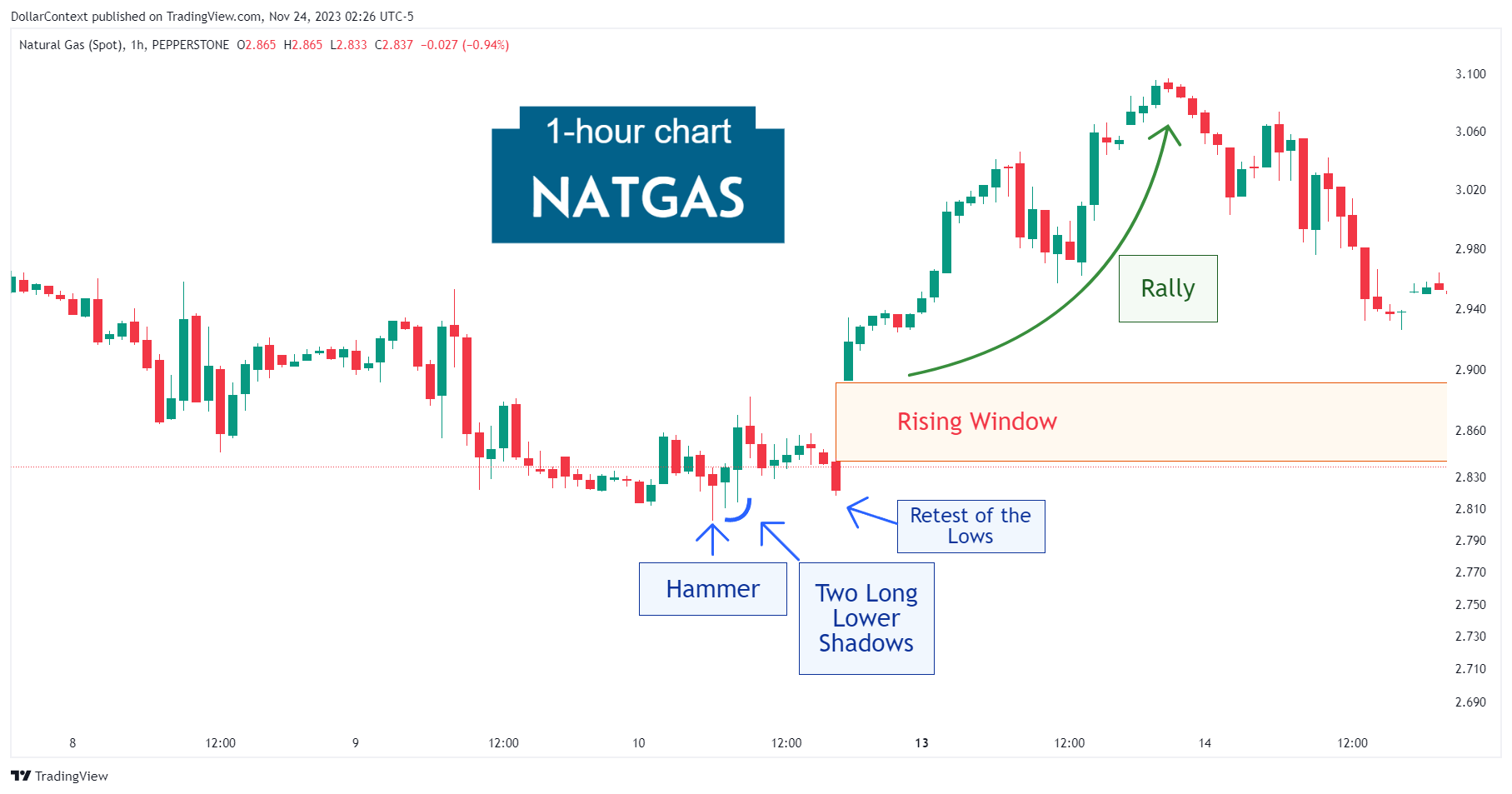
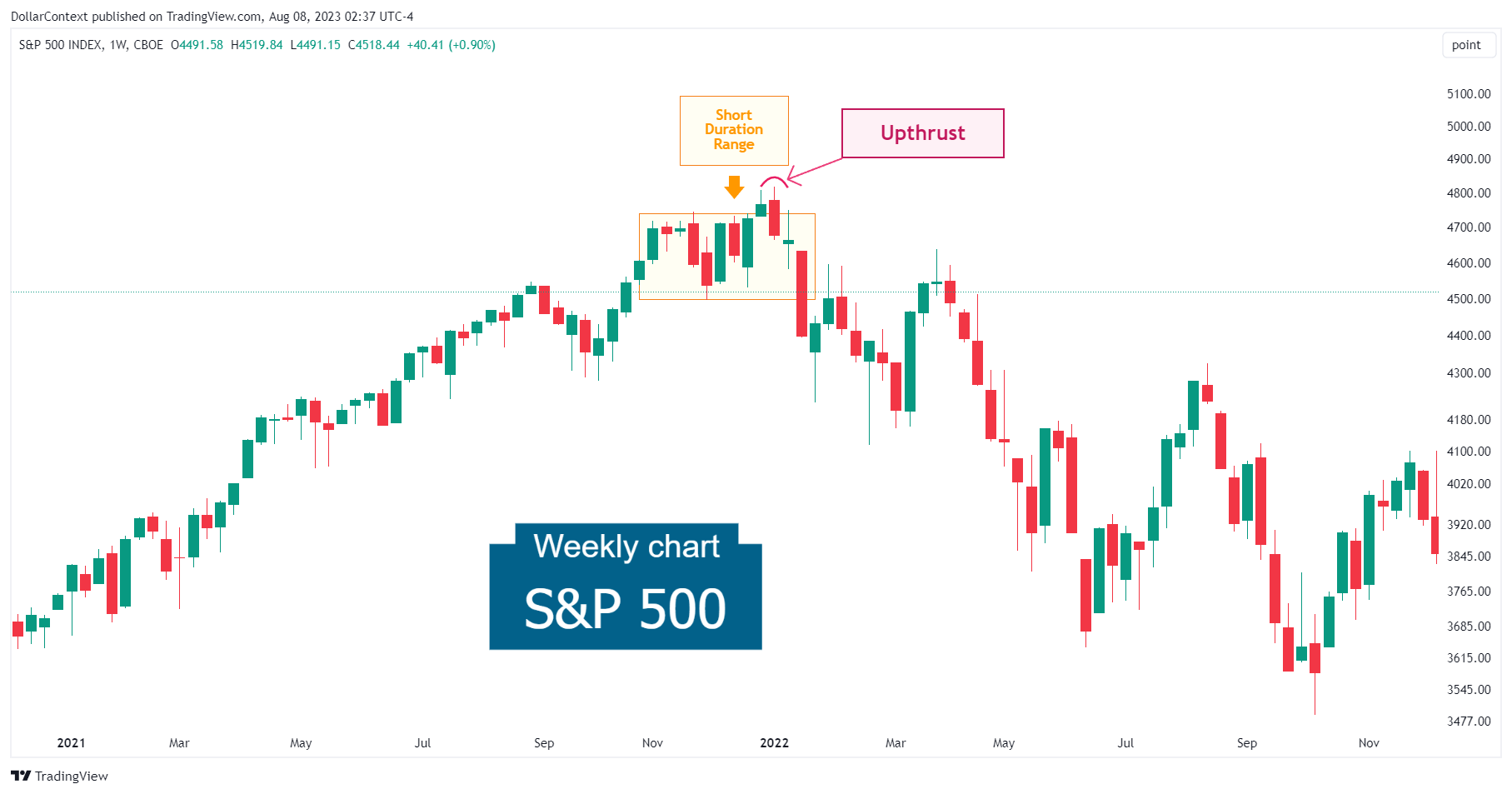
An upthrust can also emerge in the context of a short-duration trading range. In the example below, the SP500 displays a slight and temporary breach of the range after a short stint of lateral movement. Yet, this fleeting upthrust, which is also a bearish engulfing pattern, became a significant catalyst for a significant downtrend.
2.2 Speed
Based on the speed of market movements, we can categorize upthrusts into fast, medium, and slow categories.
- Fast upthrusts quickly retreat below the resistance line after breaking through.
- Slow upthrusts linger for a longer period before falling below the resistance mark.
- Medium-speed upthrusts fall in between the fast and slow categories.
2.3 Magnitude
We can also distinguish between minor and major upthrusts:
- Minor Upthrust: This occurs when the upthrust is not very pronounced. It's a minor breach of the resistance, and the price quickly falls back.
- Major Upthrust: A more significant and noticeable breach of the resistance, which might trap more traders before reversing back down.
2.4 Areas of Technical Analysis
Additionally, we can differentiate among various types of upthrusts based on the specific field (within technical analysis) that assists us in identifying the resistance area in which these upthrusts arise.
- Chart Patterns: head and shoulders pattern, double top, etc.
- Trend Analysis: uptrends, downtrends, and ranges.
- Candlestick Analysis: shooting star, evening star, dark cloud cover, etc.
- Wickoff Method: In the context of the Wyckoff Method, an upthrust is a specific price action event that is indicative of distribution and potential market weakness.
- Fibonacci's Retracements and Extensions: 23.6%, 38.2%, 50%, 61.8%, etc.
- Moving Averages and other Indicators: RSI, MACD, etc.
- Elliott Wave Theory
- Gap Analysis
- etc.
2.5 Result
Based on the outcome in terms of price action, we can identify different results after the appearance of an upthrust:
- The market retreats to the lower boundary of the trading range and continues to stay within that range.
- The market pulls back to the midpoint of the trading range and then ascends again.
- The price transitions into a distinct downtrend.
- etc.
3. Implications of an Upthrust
The failure to sustain above the resistance level and the subsequent decline signal weakness in the market's buying power. In other words, if the market is indeed weak, it shouldn’t exceed the highs established by the upthrust.
The implications of an upthrust can be outlined as follows:
- Bullish Trap: The upthrust can trap bullish traders. As prices break the resistance, bullish traders might interpret this as a genuine breakout and enter long positions. However, the rapid reversal leaves them trapped in a losing position.
- Indication of Weakness: The failure of the price to maintain levels above the resistance suggests that the bullish momentum is not strong enough to drive prices higher, signaling potential weakness in the market.
- Potential Shorting Opportunity: For traders who can identify an upthrust early, it can provide an opportunity to enter a short position, betting on a subsequent price decline.
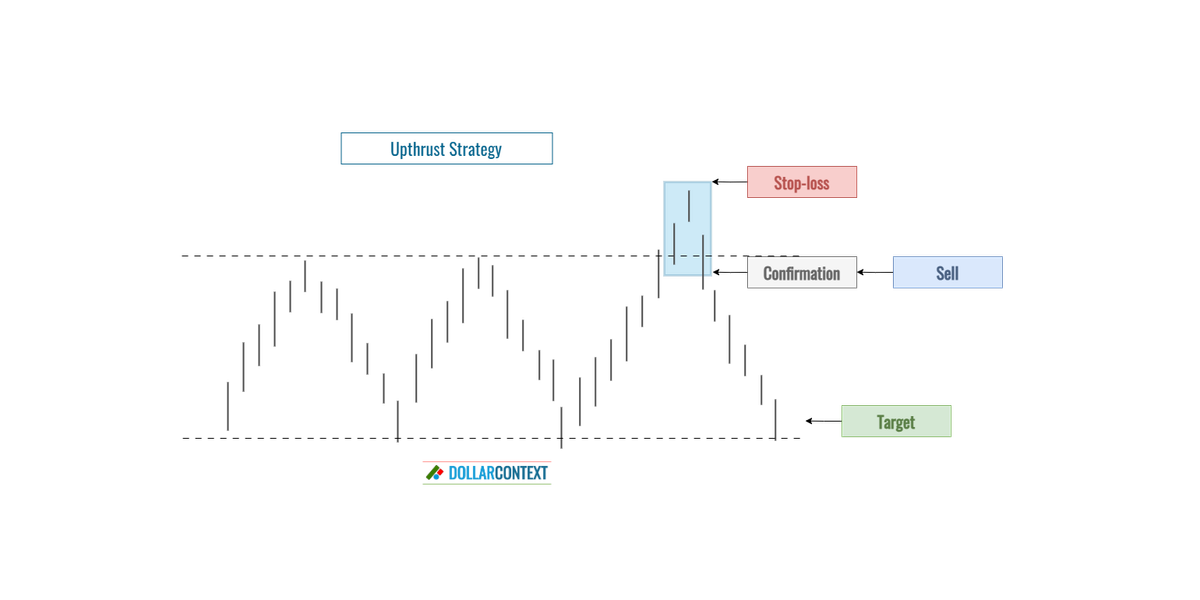
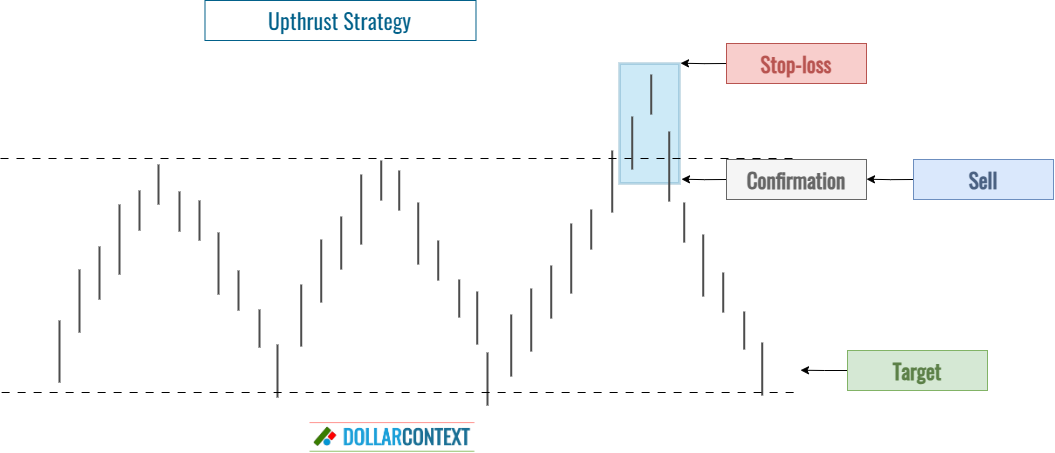
4. Trading Strategy
There is a wide range of upthrust strategies. We recommend adopting a simple strategy, such as the one detailed below.
When to open a short position
Once a potential upthrust is identified, a trader might consider entering a short position after further bearish confirmation. This could be in the form of a bearish candlestick pattern, the decline after the upthrust back into the previous range, or other bearish indicators.
Stop-loss
If a trader decides to short after an upthrust, setting a stop loss just above the high of the upthrust can be a prudent move. This way, if the price goes back up and invalidates the upthrust, the trader can limit potential losses.
Target
The target for an upthrust strategy should be based on the specific context of the trade, the risk tolerance, and the set stop-loss level. However, it’s important to keep these considerations in mind:
- If the upthrust emerges in the context of a sideways move, your trade's primary objective should be close to the range's lower boundary.
- If the upthrust arises in relation to a previously established resistance point, the initial target might be the subsequent support level beneath the one from which the upthrust originated.
5. Conclusion
The upthrust is a powerful trading concept that reflects a tug of war between bulls and bears. When the bulls fail to maintain their ground, it can provide traders with insights into the potential change in market sentiment. Like all trading strategies, upthrusts should be traded with caution, using proper risk management, and combined with other analytical tools for the best results.